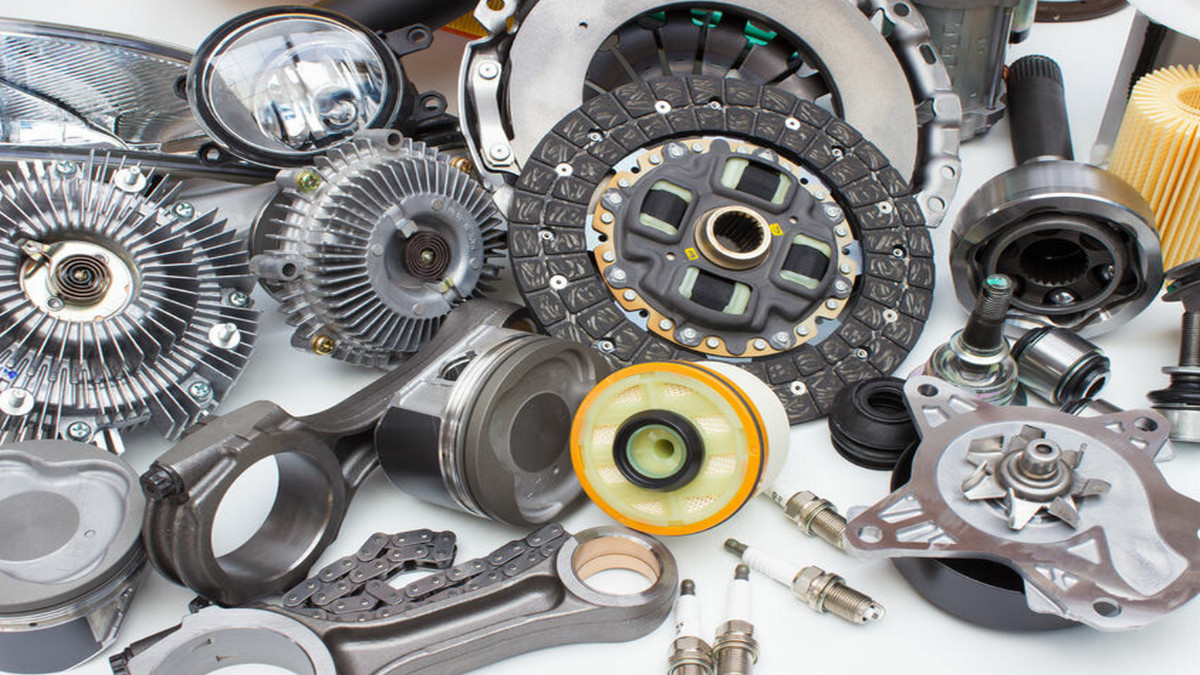
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold that contains a cavity of the desired shape and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as the casting, which is ejected or broken from the mold to complete the process. It has a wide range of applications in industrial manufacturing and in the automotive and aerospace industries.
The basic metal casting process involves creating a pattern and a mold, then pouring molten metal into the mold. You will then extract the solid metal casting and finish your piece. This process can be customized for casting different types of metals into various shapes and sizes of products.
- Sand casting
Sand casting, also known as sand molded casting, is a process of creating a mold out of sand that;incorporate a pattern into sand along in a gating system to guide the molten metal into the mold cavity. The metal is allowed to cool and then the sand is broken away from the casting to retrieve the final product. The sand used is usually made of silicon-based materials, such as synthetic sand or natural sand. Foundry sand usually consists of finely ground spherical particles that can be tightly packed together to form a smooth surface. Sand can also be strengthened by adding clay to help the particles bind more tightly. The sand allows for some degree of flexibility, to reduce the likelihood of cracking or other defects that could result from shrinkage during the cooling stage of the process.
Advantage:
Low mold cost
Wide range of uses
Ideal for making complex shapes, especially those with internal cavities
Disadvantage:
The finished product has low precision
Rough surface of casting
High cost of cleaning and processing
Application: It is often used to make crankshafts, cylinder heads and castings of automobile engine blocks.
- Lost wax casting
Lost wax casting, also known as investment casting, uses a disposable wax mold which is coated with a ceramic material that hardens around the wax mold into the shape of the casting. Once the ceramic solidifies, the casting is heated to melt the wax and the wax is drained from the mold. Molten metal is them poured into the cavity. Once the metal solidifies, the casting is broken away from the casted metal part.
Advantage:
High dimensional accuracy
Good surface finish
Parting lines are barely visible
Ability to create intricate shapes
Reduces post-casting processing costs
Disadvantage:
High production cost
Each mold can only be used for one casting
Castings are limited in size
Application: Commonly used to produce small parts with complex shapes, such as turbine engine blades.
- Vacuum die casting
Vacuum die casting is mainly used to cast high-strength, corrosion-resistant aluminum bronze. By controlling the vacuum, the pressure differential between the mold cavity and the molten metal can be varied, allowing for different fill rates required by part design and pouring requirements. Tight control of the fill rate can enhance casting stability. With proper part, mold design, and vacuum processing, voids, shrinkage, and air pockets in critical areas can also be greatly reduced or eliminated. Because the sprue is submerged under the surface of the molten metal, only pure alloy free of oxides and slag can enter the cavity, which helps produce clean, sound castings.
Advantages:
Good surface finish
High dimensionally accurate parts
Reduces voids and air bubbles in die castings
Disadvantages:
Higher cost compared to die casting
Appropriate controls are required to produce the desired results
Application: This casting method is commonly used in the automotive industry, especially for chassis forming.
- Die casting
Die casting is a method of forming materials under high pressure. Usually a two-piece mold is used. The mold is coated with a non-stick material before casting so that the mold can be separated from the casted item and reused multiple times. Die casting therefore is limited to products that can be removed from the mold without destroying the mold, as is done in other casting processes. Metals usually used are non-ferrous metals and alloys such as zinc, tin, copper and aluminum.
Advantage:
Tight dimensions and tolerances
Reduced post-processing such as machining
High dimensional consistency of manufactured parts
High quality castings
Disadvantage:
High mold cost
Long delivery time
Die castings have low plasticity
Not all metal alloys can be die cast
Applications: Die casting technology is usually used in the automotive, machine tool, and electronics industries.
- Lost foam casting
Lost foam casting is a process where ceramic material is coated around a polystyrene pattern to form a hard-shell mold. The polystyrene remains in the mold, and as molten metal is poured into the mold, heat from the metal vaporizes the polystyrene. The polystyrene vapor leaves the mold through the permeable walls of the ceramic mold. Although it is not as widely used as other processes, lost foam casting offers advantages for making intricate patterns to create a completely model-free casting that is not feasible with other processes.
Advantage:
Very complex products can be cast
High precision
Very smooth surfaces
More environmentally friendly
Short processing cycle
Disadvantage:
High cost of making patterns
Easily damaged or deformed
Application: Commonly used to make fire hydrants, valves, cylinder blocks, motor starters, etc.
- Continuous casting
Continuous casting, also called strand casting, is a casting process used for continuous mass production of metal items requiring consistency of the materials cross-section properties.
During the process, molten metal flows into and gradually passes through a casting machine which rapidly cools the metal to ensure that the solidified metal has a fine, uniform grain structure. After solidification, the cast bar is cut to desired lengths.
Advantage:
Capable of producing high quality metal
Promotes the production of standardized steel castings
Mechanized operation can reduce labor costs
Casting size and structure are easy to control
Disadvantage:
Only simple castings can be produced
Continuous cooling is required throughout the process
High investment cost
Requires a larger footprint
Applications: The most common continuous casting shapes in production are tubular and solid, but other shapes can also be produced, such as square, rectangular, hexagonal and other irregular shapes.