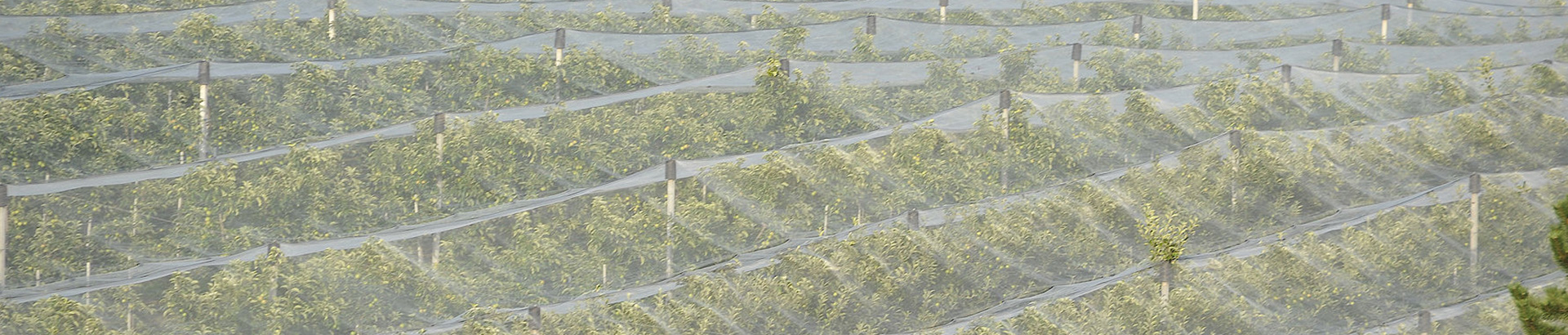
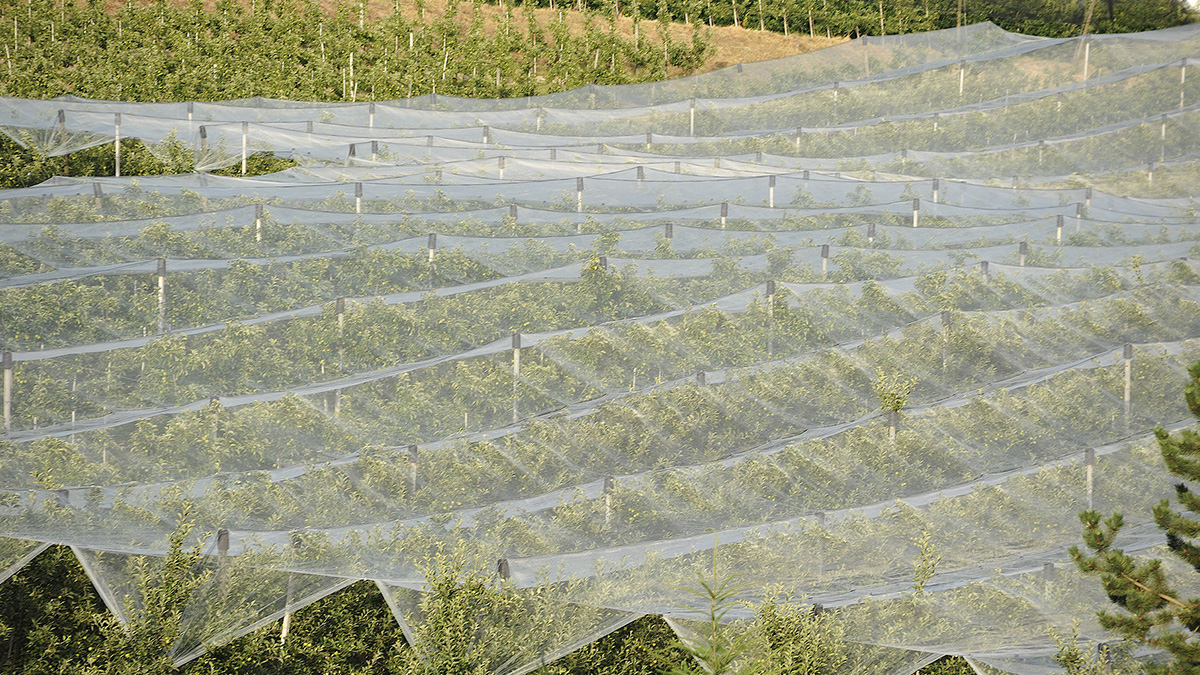
Non-woven fabrics have been produced since the early stages of the petrochemical industry. During this time, non-woven fabrics were only used for their softness and bulkiness in packaging, covering, and filling. Due to the rapid development of material science, the application scope of non-woven fabrics has expanded to various fields of industry and commerce, civil engineering, medical treatment, agriculture and environmental engineering. Its existence can be seen everywhere, especially in its very early uses in agriculture.
What Are Woven and Non-Woven Fabrics?
Non-woven fabrics are fabric-like materials made from short fibers and long fibers that have been bonded together using heat, chemical, or mechanical treatment. In general cases, woven fabrics are more durable and stronger than non-woven fabrics. There are quite a few non-woven materials, and non-woven fabric uses are seen in many industries. They have a lower barrier to production compared to woven fabric, and non-woven fabrics industries and markets are growing, developing, and maturing.
Non-Woven Industry Development
Non-woven fabric is a product that came out of the petrochemical industry after the development of plastic cloth (film). Compared with plastic cloth, it is more light-weight and has good ventilation. It is often used in medical and sanitary items such as sanitary napkins, facial towels, and filters, etc., and was later developed and applied in engineering. Non-woven fabrics are used in vegetable production to prevent cold damage.
The production process of non-woven fabric is different from plastic film, but the basic raw materials are almost the same. This includes PVC (polyvinyl chloride), PE (polyethylene), EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate copolymer), PVA (polyvinyl alcohol), and so on.
Traditional plastic film is formed into a thin film by melting the plastic and inflating it. Basically, the film is continuous; the material extends indefinitely. The surface of the film does not have any pores. It is a completely impermeable film which blocks the movement and exchange of any molecules through the film.
Following the expansion of the textile industry, artificial chemical fibers made from the above-mentioned raw materials replaced most natural plant fibers and became the darling of the textile industry. But basically, these chemical fibers are still formed into cloth through traditional warp and weft weaving.
So-called non-woven material is formed by intersecting the fibers on the same plane at various angles in all directions, instead of using traditional warp and weft methods. Compared with traditional woven fabrics, it has better material properties, and its production process can proceed from raw materials to finished products in one go. The traditional process of drawing into fibers and then weaving is saved, and the production cost is lower. Non-woven fabrics have been widely used in the apparel industry in recent years.
In recent years, due to the improvement of material science and the development of production technology, non-woven fabrics have become more diverse and used more and more widely. Different materials and products produced can be seen everywhere in our life. The expansion of the use of non-woven fabrics in agriculture is mainly due to their lightness, easy production, low cost, diversity, and wide range of applications.
Classification of Different Materials of Non-Woven Fabrics
- Long fiber non-woven fabric (with water repellency):
- Insulates against cold and frost promotes cultivation of fruit trees and vegetables by protecting them during the winter or early spring.
- Protects against insect and bird damage during early sowing or budding periods: Blocks pests during the growth period and protects against diseases and toxins transmitted by insects.
- Promotes germination by keeping seeds at the required temperature for germination.
- Short fiber non-woven fabric (with water absorption):
- Absorbent blankets in the bottom of a seedbed retain water for the roots of potted plants. Potted plants are easily moved, because the roots do not grow into the soil.
- Weed suppression mats are used as border coverings or as protection for rhizosphere soil under large woody canopies. Because of their excellent water absorption and air permeability, they can directly exchange water and air in the soil with the atmosphere. PE cloth is an excellent covering to maintain soil activity.
- The bottom of plant beds. When used in the bottom of traditional plastic plant pots, the rhizosphere of the plant has better water absorption, water permeability, and air permeability. In Japan, it is used to lay the bottom of the seedling tray for machine-transplanting. It will prevent the roots from growing into the soil, increasing the survival rate during transplanting.
- Cut fiber non-woven fabric:
- Non-woven fabric is mixed with the woven net. The fiber density of the non-woven fabric is low so that it functions similar to a woven net. Due to complicated steps in the production process, the cost is higher than that of traditional non-woven fabric. It is used for heat preservation, shading and rainproofing, insect-proofing, and wind-proofing.
Applications of Non-Woven Fabrics in Agricultural Industry
Non-woven fabrics were first applied to agriculture in Europe in 1978 to keep carrots warm for early harvesting, and to prevent tomato leaf viruses and whiteflies.
In the United States non-woven fabrics are used for the mulching of cantaloupes, sweet peppers, tomatoes, root vegetables, carrots, radishes, cabbage, lettuce, and other vegetables. It is mainly used for heat preservation, promoting early harvesting, and insect control. Because non-woven materials can help to increase soil temperature and have good water retention, they are used for surface covers such as grass-proof mats. Short fiber is also used to produce water absorbent blankets which are applied to nursery beds, so that the roots can fully absorb water. They can also be used as the bottom medium for turf production, or directly used as garden grassland for moisturizing, draining, and dividing the garden. They are also used as planting bags for large woody plants such as garden trees and fruit trees, preventing weeds and retaining moisture.
In Taiwan, in addition to the above-mentioned functions, non-woven fabrics are used in crop covering. They are also widely used in the environmental control of large greenhouses to save energy. Double-layered coverings and canopy curtains reduce radiation and heat dissipation at night. High-density spun-bonded non-woven TAVIK fabrics were used in the early days to protect and shade cauliflower bulbs. Because of its high shading ability, low thermal conductivity, and easy recyclability, it was quickly accepted by farmers. Later, it was gradually applied to the heat preservation and insect-proof cultivation of leaf vegetables, and the shade and heat preservation and cultivation of fruit trees and pineapples. However, due to Taiwan's unique climate and ecology, the development of the non-woven industry has been slow. Taiwan non-woven fabric manufacturers continue to innovate non-woven technology, with focus on air permeability, water absorption, and water repellency of non-woven fabrics. For its use in the preservation and storage of agricultural products, it has strengthened its research and hopes to develop a wider range of applications.
Difficulties in the Applications of Non-Woven Fabrics in Agriculture
- Crop diversity:
Each crop has different plant types and physiological characteristics. It is important to choose materials and use methods according to the needs of the crop.
- Cultivation mode:
In Taiwan's vegetable production, due to the variety of crops, cultivation modes are very diversified. It will be a big test to develop methods for heat preservation in winter and covered cultivation during the summer, high-temperature period.
- How to apply:
- Application in the greenhouse: Consider its heat preservation, light transmittance, and weather resistance.
- Application in the greenhouse: Consider its heat preservation, light transmittance, and weather resistance.
- Open field cultivation: How to fix the floating cover to prevent it from being lifted by the wind, and choosing the right crops must be taken into consideration.
- Selection of the beginning period of coverage: Depending on the purpose of coverage, appropriate consideration should be given to the period of coverage. Such as covering immediately after sowing in order to promote germination; or covering at the seedling stage; or after transplanting; or pre-harvesting treatment. All must be selected according to different cultivation purposes.
- Timing of cover removal: According to the variations of different crops, cultivation modes, cultivation periods, and meteorological conditions, the timing of cover removal should be properly judged for the desired effect.
- Covering period: Weather conditions must be considered when deciding when to cover and remove coverage of crops.
- Changes in weather during the coverage period: Meteorological conditions cannot be controlled; therefore, it is necessary to always pay attention to the changes of weather and the growth progress of crops.
- The control of pests and diseases: Basically, covering crops with non-woven fabrics tends to reduce the occurrence of pests and diseases. This is based on the premise that there is no pathogenic bacteria or insect source before the coverage.
The Benefits of Non-Woven Fabrics Uses in Agriculture
Non-woven fabric is a material that has potential for application in the agricultural industry due to its convenience of use and effectiveness.
- Prevent bird damage: Floating cover can be used to prevent bird damage to vegetable seeds and crops.
- Anti-cold and frost damage: Non-woven floating covers can effectively prevent cold and frost damage to crops that are prone to them.
- Used for heat preservation of cover crops in winter to promote growth.
- To prevent pests: Floating cover on vegetables can prevent or reduce pests.
- As a transplanting bowl for seedlings: It can be easily transported and improves the survival rate of seedlings.
- Prevent sunburn: Use on fruit trees to prevent sunburn caused to fruits.
- Preservation: In the post-harvest processing of garden products, it can be used to preserve the freshness of the products.
- Bagging: It can be used as fruit bagging to prevent pests, bird damage, heat damage, and color change.
There is a lot of room for development in the application of non-woven fabrics in agriculture. We should strengthen research for the development of its material, and according to different regions, seasonal weather characteristics, and the purpose of production and cultivation, we should make appropriate choices of covering materials in order to make the non-woven fabric most effective.