What Kinds of Plastic Blow Molding Processes Are There?
What Is Blow Molding?
Blow molding mainly refers to hollow blow molding, which is a method of inflating hot-melt plastic enclosed in a mold to form a hollow product using gas pressure. Blow molding requires the use of a concave mold. Compared with injection molding, equipment costs are lower, adaptability is greater, the moldability is good, and products with complex curves and shapes can be molded.
During blow molding, a hollow, semi-molten tube blank (or parison) is extruded and placed into a mold. The mold is then closed and compressed air is blown into the tube blank to extend and expand it to the sides of the mold. The plastic cools, maintaining the shape of the mold. In general, blow molding is done with low pressures so there is little wear on the mold and production efficiency is high, but control of cycle time is critical.
Material Requirements for Blow Molding Process:
High-quality raw material for hollow blow molding will have a melt index of 0.04 to 1.12. Commonly used materials are polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, polyamide, cellulose acetate, and polyacetal resin, of which polyethylene is used the most.
What Are the Various Uses of Blow Molding?
Blow molding is a common method for forming plastic packaging containers, water bottles, juice and milk bottles, shampoo bottles, automotive parts, portable picnic coolers, or any other types of hollow plastic products.
-
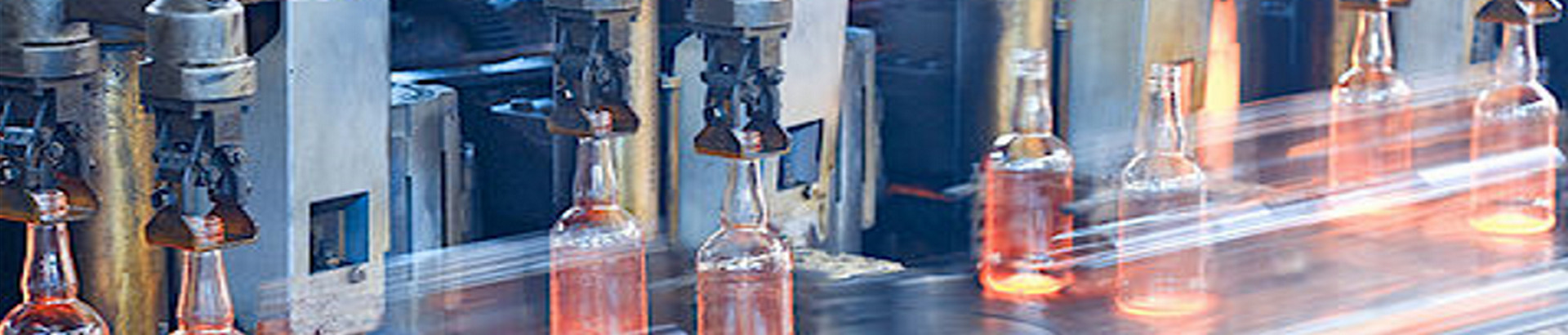
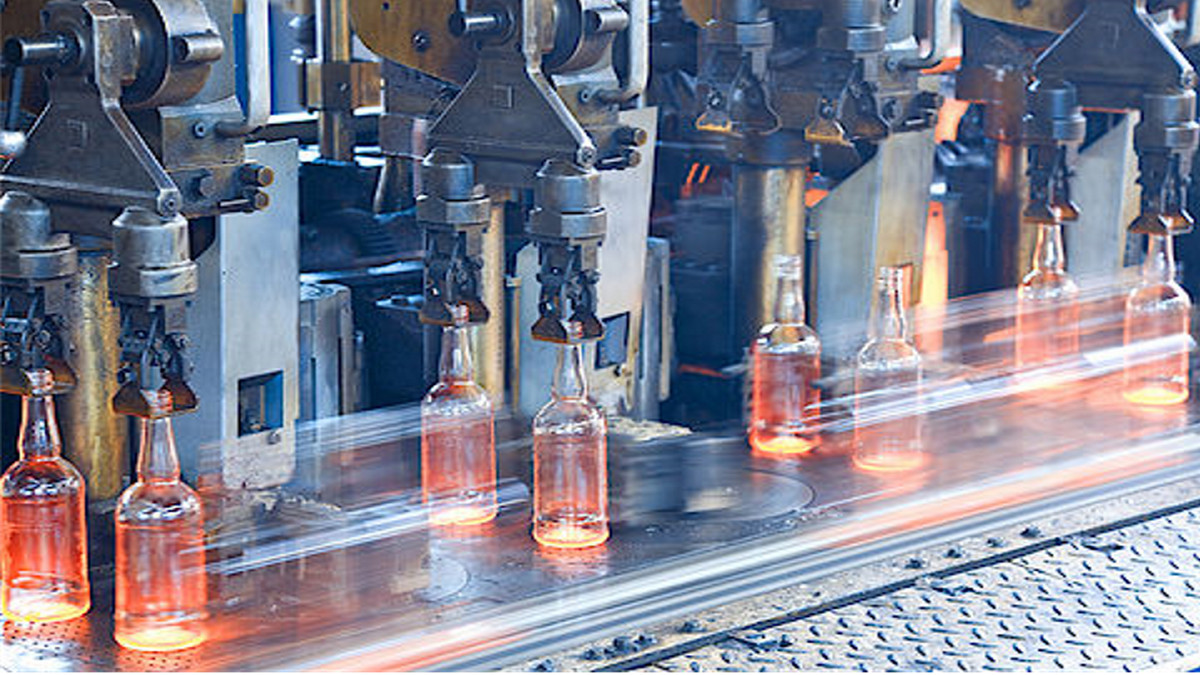
Extrusion blow molding:
Extrusion blow molding is most widely used for plastic packaging and container forming. The thermoplastic pellets or powder, are plasticized by an extruder and pressed through a die to prepare a hot-melt tubular parison. When the parison reaches a predetermined length, it enters the mold and the mold is closed. Air is then blown into the parison to press the melted plastic against the sides of the mold to form it into the desired container.
Extrusion blow molding gives high production efficiency, has a large allowable range for shapes, sizes, and wall thicknesses, and is highly adaptable. High strength blow molded products can be made with simple equipment and low investment. One drawback of extrusion blow molding it that precision of the product is not high. Thickness of the plastic can vary as it is stretched, and there will be a seam at the bottom of the container. -
Injection blow molding:
With injection blow molding, instead of the plastic passing through a die to form a tube, a single parison is injected into the mold cavity. Air is blown into the parison to expand it out to the surface of the mold where it will solidify. After cooling and setting, the product is taken out.
Advantages of injection blow molding is that there is no splicing seam, and no post-dressing is required; the dimensional accuracy of the thread and bottle mouth is high, and the inner wall of the neck is a smooth cylindrical surface; output volume can be very large; the bottom of the product has high strength with less material loss; and the wall will have more uniform thickness. However, the investment required for equipment is large, the processing and production cycle is longer than with the extrusion method, the requirements for operators are high, the shape cannot be too complicated, and the size of the container is limited. It is suitable for the production of small precision containers. Medicinal plastic bottles and jars are often formed by this method. -
Stretch blow molding:
Stretch blow molding is a molding method most often used to form beverage containers. The parison will have a preformed bottle mouth. The parison is heated to an appropriate temperature and placed in the mold and a stretch rod is inserted into the mouth of the parison to stretch it to the bottom of the mold. Air is then blown into the parison to stretch or out to the sides of the mold. By using the stretch molding method, as the plastic is stretched, macromolecules in the plastic are oriented in a way that greatly improves the strength and performance of the plastic container.
With stretch blow molding there is high production efficiency, easy weight control, and little scrap. Most PP bottles and PET bottles such as beverage bottles, are formed by injection stretch blowing. The product has high impact toughness, good rigidity, good transparency and gloss, good barrier properties, and airtightness. Stretch blow molding requires accurate control of the stretching temperature so the investment cost for equipment is high. -
Multilayer blow molding:
Multi-layer blow molding is used for preparing multi-layer containers through a blow molding process using a multi-layer composite parison. Some inherent shortcomings of single-layer plastic containers can be overcome by using multiple plastic layers.
The multi-layer blow molding method can improve the performance and physical and mechanical properties of plastic containers, such as shading, heat insulation, reducing flammability, improving printability, etc.